1. About this Guide
This guide will walk you through the installation and configuration of the native Microsoft Outlook compatibility layer SOGo offers.
Prior going over this guide, you should have a working SOGo installation. Please refer to the SOGo Installation and Configuration Guide for more information on installing and configuring SOGo.
This guide also includes instructions for configuring Microsoft Outlook with SOGo.
The instructions are based on version 2.3.22 of SOGo.
The latest version of this guide is available at http://www.sogo.nu/downloads/documentation.html.
2. Introduction
SOGo is a free and modern scalable groupware server. It offers shared calendars, address books, and emails through your favourite Web browser and by using a native client such as Mozilla Thunderbird and Lightning.
SOGo is standard-compliant. It supports CalDAV, CardDAV, GroupDAV, iMIP and iTIP and reuses existing IMAP, SMTP and database servers — making the solution easy to deploy and interoperable with many applications.
SOGo features:
-
Scalable architecture suitable for deployments from dozen to many thousand users
-
Rich Web-based interface that shares the look and feel, the features and the data of Mozilla Thunderbird and Lightning
-
Improved integration with Mozilla Thunderbird and Lightning by using the SOGo Connector and the SOGo Integrator
-
Native compatibility for Microsoft Outlook 2003, 2007, 2010, and 2013
-
Two-way synchronization support with any Microsoft ActiveSync-capable device, and Outlook 2013
SOGo is developed by a community of developers located mainly in North America and Europe. More information can be found on http://www.sogo.nu/.
3. Architecture
The following diagram demonstrates the architecture of the native Outlook compatibility layer of SOGo.
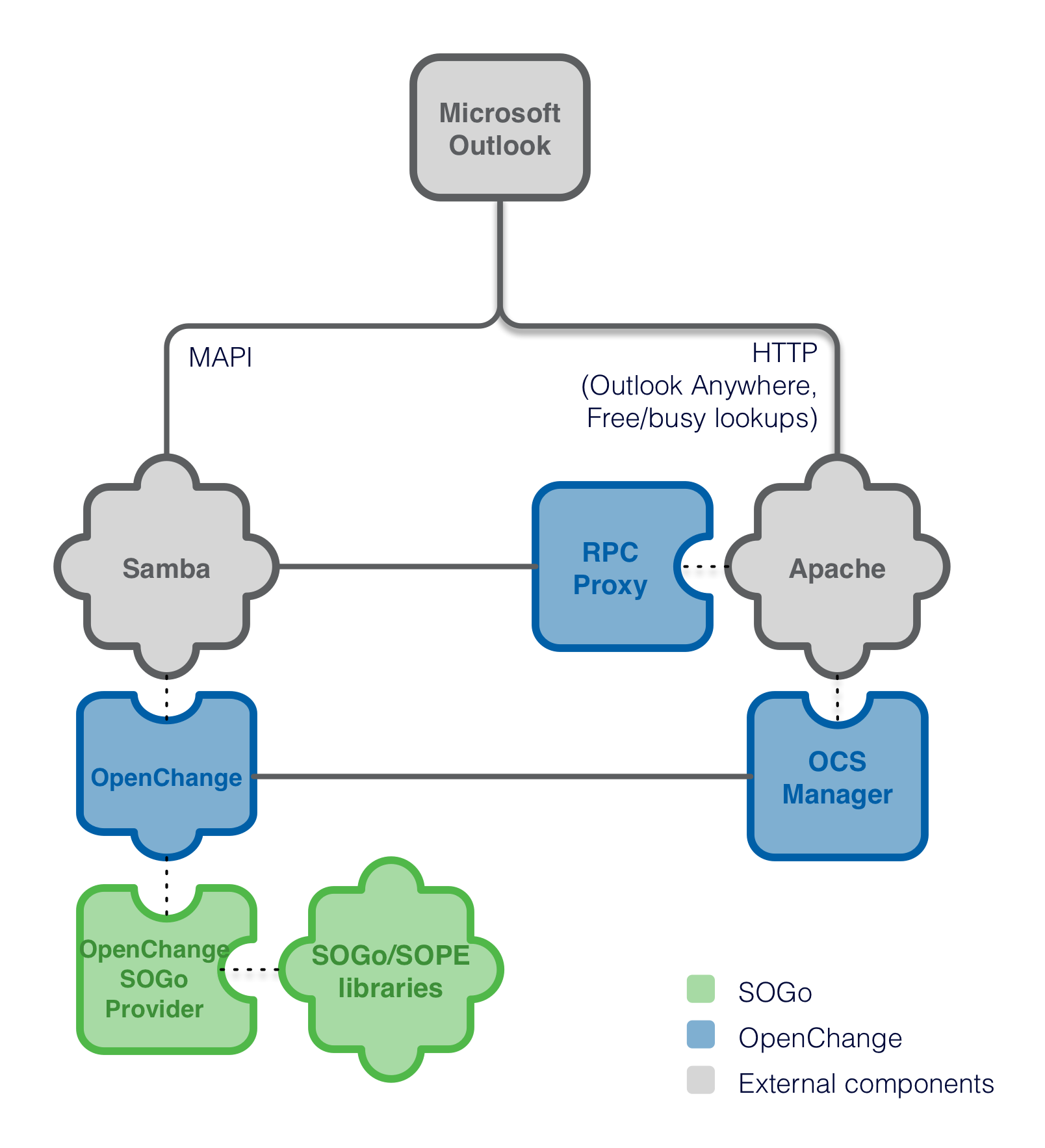
With Samba 4 and OpenChange, Microsoft Outlook clients can communicate natively with SOGo using the Microsoft Exchange protocol, without requiring costly and hard-to-maintain third-party MAPI connectors for Microsoft Outlook.
4. Requirements
Organizations generally have solutions to authenticate users such as LDAP servers or Microsoft Active Directory servers.
The solution being used will influence how users are provisioned in Samba 4, a key component for native Outlook compatibility in SOGo.
4.1. LDAP Server
If your organization uses a LDAP server such OpenLDAP, Novell eDirectory, Apache Directory or any other solution, you must use Samba 4’s internal directory server and synchronize the data between both.
Synchronization scripts are not provided and unless you have clear-text passwords of your existing users, they will have to be changed during your initial synchronization so that your LDAP’s server passwords are identical to the ones from Samba 4.
Any modifications to your existing LDAP server (password change, user addition or deletion, etc.) will have to be replicated to Samba 4’s internal directory server.
Note that if you install Samba 4 on a server that is already running a LDAP service, you will have to change to TCP port on which your LDAP server listens to. Samba 4 will use the TCP port 389 and it can’t be changed.
For example, with OpenLDAP, you can use the -h parameter for slapd
to make it listen on an other TCP port.
4.2. Microsoft Active Directory
If your organization uses Microsoft Active Directory, Samba 4 will need to be joined to your Active Directory domain, as a DC.
Samba 4 will be able to reuse all the information contained in Microsoft Active Directory and no synchronization process needs to be put in place as information will get replicated to Samba 4 automatically.
For more information on joining Samba 4 to an existing Microsoft Active Directory domain, please refer to the Samba 4 documentation available at the following URL:
More specifically, have a look at the samba-tool domain join command.
Note that joining Samba 4 to your Active Directory domain as a member
will currently not work. An authentication bug is present in Samba 4
which then prevents all Outlook users to successfully authenticate
through Samba 4. This issue has been reported to the Samba team and is
being worked on.
4.3. Other or No Solution
If your organization neither uses a LDAP server or Microsoft Active Directory, you can start using Samba 4 as your directory server.
Samba 4’s directory can be queried over LDAP just like Microsoft Active Directory and can also serve as a domain controller for Windows-based environments.
For example, SOGo can very well use Samba 4’s built-in directory server to authenticate users. A SOGoUserSources entry to achieve this wold look like this:
su – sogo
defaults write sogod SOGoUserSources '(
{
CNFieldName = displayName;
IDFieldName = cn;
UIDFieldName = sAMAccountName;
baseDN = "cn=Users,dc=example,dc=com";
bindDN = "cn=Administrator,cn=Users,dc=example,dc=com";
bindFields = (
sAMAccountName
);
bindPassword = "%1OpenChange";
canAuthenticate = YES;
displayName = "Shared Addresses";
hostname = "127.0.0.1";
id = samba;
isAddressBook = YES;
port = 389;
}
)'
Please refer to the SOGo Installation and Configuration Guide for more
information regarding SOGoUserSources.
4.4. IMAP Server and Trust
An IMAP server supporting the ACL, UIDPLUS and QRESYNC IMAP extensions is required, such as Cyrus IMAP version 2.4 or later, or Dovecot version 2.1 or later. If your current IMAP server does not support these extensions, you can use Dovecot’s proxying capabilities. The follow configuration example makes Dovecot proxy all IMAP request to an existing server:
auth_mechanisms = plain login
imapc_host = inverse.ca
imapc_port = 993
imapc_ssl = imaps
imapc_ssl_verify = no
mail_gid = imapproxy
mail_home = /home/imapproxy/%u
mail_location = imapc:~/imapc
mail_uid = imapproxy
passdb {
args = host=inverse.ca ssl=imaps port=993 ssl_ca_dir=/etc/pki/tls/certs
default_fields = userdb_imapc_user=%u userdb_imapc_password=%w
driver = imap
}
protocols = imap
ssl = no
userdb {
driver = prefetch
}
SOGo would then be configured to use Dovecot’s proxy as the IMAP server.
Moreover, the authentication mode in use by Windows with Samba and Exchange servers prevent the backend from knowing the real password being used by the user. This implies that the IMAP server must accept any passwords from the host on which Samba is running.
To accomplish this with Cyrus IMAP Server, set sasl_pwcheck_method
to alwaystrue in /etc/imapd.conf. You should restrain this to
an imapd instance dedicated to SOGo.
For Dovecot, use an authentication source similar to:
passdb {
driver = static
args = nopassword=y allow_nets=127.0.0.1/32
}
You should also make sure that you restrain this only to the SOGo processes.
For any other IMAP server, refer to the product’s documentation. If such capability is not offered, you can alternatively define the cleartext password for each user. Please refer to the Adding Users section from this document.
5. Installation
This section will guide you through the installation of the native Microsoft Outlook compatibility layer SOGo offers.
5.1. Debian 8 (Jessie) and Ubuntu 14.04 (Trusty Tahr)
Please follow the instructions from http://www.sogo.nu/english/downloads/backend.html to setup your apt sources.
Then install Samba 4 on top of an existing SOGo installation:
apt-get update apt-get install samba samba-dev
Once completed, install the packages related to OpenChange and the SOGo provider:
apt-get install openchangeserver \
sogo-openchange \
openchangeproxy \
python-ocsmanager \
mysql-server \
python-mysqldb \
openchange-ocsmanager \
openchange-rpcproxy \
python-sievelib \
python-spyne \
python-rpclib
Once the packages are installed, refer to the Configuration chapter from this guide.
|
Note
|
The ocsmanager.conf and rpcproxy.conf are currently located in
/etc/apache2/conf.d. These should be moved to /etc/apache2/conf-available.
This is a packaging error that will soon be fixed.
|
|
Note
|
You might have to adjust the rpcproxy.conf configuration file to add the
Require all granted permission if you get Apache errors such as
client denied by server configuration.
|
6. Configuration
In this section, you’ll learn how to configure the native Microsoft Outlook compatibility layer that SOGo offers.
6.1. SOGo Configuration
First thing to do is to configure SOGo to use your current services, which are your IMAP, SMTP and SQL database servers. The configuration instructions for this are available in the SOGo Installation and Configuration Guide available from http://www.sogo.nu/.
Please refer to that documentation before continuing with the instructions included in this guide.
6.2. Samba 4 Configuration
Run the following commands as root:
samba-tool domain provision --realm=example.com \
--domain=EXAMPLE \
--adminpass='%1OpenChange' \
--server-role='domain controller'
samba-tool user setexpiry administrator --noexpiry
You might consider changing the realm and domain used, to suit your environment.
You might also have to
remove /etc/samba/smb.conf prior running this command.
Add the following parameters to the [global] section of the
/etc/samba/smb.conf configuration file:
### Configuration required by OpenChange server ### dsdb:schema update allowed = true dcerpc endpoint servers = epmapper, mapiproxy, dnsserver dcerpc_mapiproxy:server = true dcerpc_mapiproxy:interfaces = exchange_emsmdb, exchange_nsp, exchange_ds_rfr ### Configuration required by OpenChange server ###
Your Samba 4 configuration file should look like this:
# Global parameters [global] server role = active directory domain controller workgroup = EXAMPLE realm = example.com netbios name = sogo passdb backend = samba4 ### Configuration required by OpenChange server ### dsdb:schema update allowed = true dcerpc endpoint servers = +epmapper, +mapiproxy dcerpc_mapiproxy:server = true dcerpc_mapiproxy:interfaces = exchange_emsmdb, exchange_nsp, exchange_ds_rfr ### Configuration required by OpenChange server ### [netlogon] path = /var/lib/samba/sysvol/example.com/scripts read only = No [sysvol] path = /var/lib/samba/sysvol read only = No
6.3. OpenChange Configuration
Since v2.2, OpenChange stores its metadata in MySQL so you need to have it installed.
First, create the OpenChange MySQL user:
$ mysql -u root -p mysql> CREATE USER 'openchange-user'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'openchange$123'; mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON `openchange`.* TO 'openchange-user'@'localhost' WITH GRANT OPTION; mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
The Samba AD schema needs to be filled with additional object definitions by running the following commands:
openchange_provision --standalone NOTE: This operation can take several minutes [+] Step 1: Register Exchange OIDs [+] Step 2: Add Exchange attributes to Samba schema [+] Step 3: Add Exchange auxiliary classes to Samba schema [+] Step 4: Add Exchange objectCategory to Samba schema [+] Step 5: Add Exchange containers to Samba schema [+] Step 6: Add Exchange *sub* containers to Samba schema [+] Step 7: Add Exchange CfgProtocol subcontainers to Samba schema [+] Step 8: Add Exchange mailGateway subcontainers to Samba schema [+] Step 9: Add Exchange classes to Samba schema [+] Step 10: Add possSuperior attributes to Exchange classes [+] Step 11: Extend existing Samba classes and attributes [+] Step 12: Generic Exchange configuration objects [+] Step 13: Finalize generic Exchange configuration objects [SUCCESS] Done! [+] Step 1: Exchange Samba registration [SUCCESS] Done! [+] Step 1: Register Exchange Samba as the main server [SUCCESS] Done!
Create the OpenChange database:
openchange_provision --openchangedb --openchangedb-uri 'mysql://openchange-user:openchange$123@localhost/openchange' Setting up openchange db [+] Public Folders =================== * Public Folder Root : 0x0100000000000001 (72057594037927937) * IPM_SUBTREE : 0x0200000000000001 (144115188075855873) * NON_IPM_SUBTREE : 0x0300000000000001 (216172782113783809) * EFORMS REGISTRY : 0x0400000000000001 (288230376151711745) * OFFLINE ADDRESS BOOK : 0x0500000000000001 (360287970189639681) * /o=First Organization/cn=addrlists/cn=oabs/cn=Default Offline Address Book: 0x0600000000000001 (432345564227567617) * SCHEDULE+ FREE BUSY : 0x0700000000000001 (504403158265495553) * EX:/o=first organization/ou=first administrative group: 0x0800000000000001 (576460752303423489) * Events Root : 0x0900000000000001 (648518346341351425)
Finally, modify /etc/samba/smb.conf to specify OpenChange connection information
for its indexing database. Add the following at the end of the [global] section:
mapistore:namedproperties = mysql namedproperties:mysql_user = openchange-user namedproperties:mysql_pass = openchange$123 namedproperties:mysql_host = localhost namedproperties:mysql_db = openchange mapistore:indexing_backend = mysql://openchange-user:openchange$123@localhost/openchange mapiproxy:openchangedb = mysql://openchange-user:openchange$123@localhost/openchange
Next, you can start Samba using the usual command:
/etc/init.d/samba start
On upstart-based distributions, use:
start samba-ad-dc
You can also launch the OpenChange web services:
/etc/init.d/openchange-ocsmanager start
6.4. Apache Configuration for Web Services
The OpenChange web services consist of two components:
-
OCS Manager which is used for autodiscovery and freebusy lookups on Outlook 2007 and 2010. This service runs in its own application server which listens on
127.0.0.1:5000by default. Apache needs to be configured to forward certain requests to it to make it accessible from the outside. Note that this service MUST be accessible over*HTTPS*, otherwise Outlook won’t use it. -
RPC Proxy which is used for RPC over HTTP ("Outlook Anywhere"). This service runs as a WSGI application under apache (mod_wsgi). While HTTPS is not required to access this service, it is strongly recommended.
For Debian-based distributions, these files can be found
in /etc/apache2/conf.d/ or /etc/apache2/conf-available.
The configuration requires three Apache modules: mod_proxy, mod_proxy_http and mod_wsgi. These are usually already installed but might need to be activated on Debian-based installations:
a2enmod proxy proxy_http wsgi
The OCS Manager and RPC Proxy configuration module can be enabled using:
a2enconf ocsmanager a2enconf rpcproxy
The reqtimeout apache module is known to cause problems when using the default configuration shipped with Debian-based systems. On such distributions, Apache will close (HTTP/1.1 500) any HTTP request for which the HTTP body hasn’t arrived in 10 seconds.
While this is arguably good practice with regular HTTP, it will disrupt the RPC over HTTP protocol implemented by RPC Proxy: Outlook will continuously disconnect and reconnect leading to suboptimal performance.
To avoid this problem, use a much higher timeout or disable the module:
a2dismod reqtimeout
You should now restart the Apache service and make sure it will start on boot.
On Debian-based distributions, do:
update-rc.d apache2 defaults && /etc/init.d/apache2 restart
Finally, you must adjust the OCS Manager configuration file, which is
located in /etc/ocsmanager/ocsmanager.ini. You should enable LDAP-based
authentication in the main section and configure it accordingly. You should
also enable rpcproxy. You file should be similar to this one:
[DEFAULT]
debug = true
email_to = you@yourdomain.com
smtp_server = localhost
error_email_from = paste@localhost
[main]
auth = ldap
mapistore_root = /var/lib/samba/private
mapistore_data = /var/lib/samba/private/mapistore
debug = yes
[auth:file]
[auth:ldap]
host = ldap://127.0.0.1
port = 389
bind_dn = cn=administrator,cn=Users,dc=example,dc=com
bind_pw = %1OpenChange
basedn = cn=Users,dc=example,dc=com
[auth:single]
username = openchange
password = {SSHA}I6Hy5Wv0wuxyXvMBFWFQDVVN12_CLaX9
[server:main]
use = egg:Paste#http
host = 127.0.0.1
port = 5000
protocol_version = HTTP/1.1
[app:main]
use = egg:ocsmanager
full_stack = true
static_files = true
cache_dir = %(here)s/data
beaker.session.key = ocsmanager
beaker.session.secret = SDyKK3dKyDgW0mlpqttTMGU1f
app_instance_uuid = {ee533ebc-f266-49d1-ae10-d017ee6aa98c}
NTLMAUTHHANDLER_WORKDIR = /var/cache/ntlmauthhandler
SAMBA_HOST = 127.0.0.1
[rpcproxy:ldap]
host = localhost
port = 389
basedn = CN=Users,DC=example,DC=com
set debug = true
[autodiscover] [autodiscover:rpcproxy] enabled = true [outofoffice] [outofoffice:file] sieve_script_path = /var/vmail/$domain/$user/sieve-script sieve_script_path_mkdir = false [outofoffice:managesieve] secret = secret [loggers] keys = root [handlers] keys = console [formatters] keys = generic [logger_root] level = INFO handlers = console [handler_console] class = StreamHandler args = (sys.stderr,) level = NOTSET formatter = generic [formatter_generic] format = %(asctime)s %(levelname)-5.5s [%(name)s] [%(threadName)s] %(message)s
Once completed, start the OCS Manager service:
/etc/init.d/openchange-ocsmanager start
6.5. Name Service Configuration for Web Services
The autodiscovery service must be made accessible in order to advertise the web services provided by OpenChange. This can be done in two ways.
-
The first is to associate the FQDN
autodiscover.example.com.with the machine that hosts Samba 4 / OpenChange, by adding aCNAMEentry in your DNS configuration. Note that, instead or changing your DNS server configuration, you can simply add a similar entry to the hosts file of the Windows machine from where you’ll run Outlook, which is handy for testing purposes. -
The second option is to add a
SRVentry to your DNS configuration where the_servicevalue would beAutodiscoverand the_protocolwould be_tcp.
For example:
_autodiscover._tcp.example.com. IN SRV 0 0 443 sogo.example.com.
Again, the autodiscovery service must be accessible over HTTPS.
7. Adding Users
Users that wish to connect natively to SOGo must be provisioned in Samba 4 and in OpenChange – even if they already exist in your current LDAP or Microsoft Active Directory server.
To add a user, execute the following commands:
# add user to samba samba-tool domain passwordsettings set --complexity=off samba-tool domain passwordsettings set --min-pwd-length=1 samba-tool user add <username> samba-tool user setexpiry <username> --noexpiry # create user in openchange openchange_newuser --create <username>
If you don’t have a trust between your IMAP server and SOGo, you must at
this point set the cleartext password of the newly created user in
/var/lib/samba/private/mapistore/<username/password.
This per-user file contains the cleartext password of the user as a UTF-8 string, on a single line. This password will be used to authenticate SOGo/OpenChange storage provider to your IMAP server.
8. Microsoft Outlook Configuration
To connect Microsoft Outlook, you can either use the IP address of the
server or its DNS name. If you prefer using the DNS name, add an entry
like the following to the c:\windows\system32\drivers\etc\hosts file
in order to associate the IP address with the right DNS names:
192.168.1.1 sogo.example.com autodiscover.example.com
Next, you must configure Microsoft Outlook.
-
Open the Control Panel ⇒ Mail ⇒ Email Accounts.
-
Select Add a new e-mail account
-
Choose Microsoft Exchange Server
-
Fill the required information. Enter the DNS name or the IP address of your SOGo server in the Microsoft Exchange Server field
-
Leave the Use Cached Exchange Mode checkbox enabled
-
Enter your username in the User Name field
-
Click on More Settings and ignore the warning, if any, about Exchange being offline by clicking on Cancel
-
From the Security tab, enable Always prompt for user name and password
-
From the Connection tab, enable "Outlook Anywhere" if you plan to use Outlook outside of your LAN. Moreover, click on the Exchange Proxy Settings… button to enable it for slow and fast networks. Specify also the host, which should be the same value you specified in the Microsoft Exchange Server field.
-
Finally, click on Check Name and confirm your username and password
Start Microsoft Outlook and enter your username and password. It will start to synchronize your mailbox. This could take a long time if you have many emails, events, tasks and contacts. Once this step is completed, check the autodiscovery service with Outlook 2007 or 2010 by simultaneously holding the CTRL key on your keyboard and right-clicking on the Outlook icon in the notification toolbar. A special entry named "Test E-mail AutoConfiguration…" will appear and will enable you to check the service.
9. Known Issues or Limitations
-
Make sure you periodically backup all your data regarding SOGo.
-
Make sure you have no firewalls activated between your Microsoft Outlook clients and the SOGo server with Native Outlook Compatibility module. If you do, use "Outlook Anywhere" to connect Outlook to SOGo/OpenChange.
9.1. Current Limitations
The current version of the Native Microsoft Outlook compatibility layer has some limitations.
Those limitations will be overcome in the upcoming releases. If you are interested in having those limitations fixed more rapidly, please contact Inverse by sending an email to support@inverse.ca.
9.1.1. General
-
If you can’t see any email’s content with Microsoft Outlook 2007, install the latest Service Pack available from Microsoft’s website for this specific version. Microsoft Outlook 2007 (12.0.6423.100) SP2 MSO (12.0.6425.1000) is known to work.
-
When you create a new Microsoft Outlook profile, not all folders might be synchronized during the first start. Simply select the appropriate folder and click "Send and Receive". Synchronizing a folder may take some time. For example, a folder with 1000 email messages might take around 5 minutes based on the underlying hardware.
-
Errors when synchronizing the "Offline Address Book" are normal and can be ignored for now. This feature is currently not supported.
-
If you face strange issues from Microsoft Outlook, you might want to remove any data associated with the user from the SOGo server and recreate a Microsoft Outlook profile. To remove any data associated to a user, use the
openchange_user_cleanupscript distributed with OpenChange. The script can be found in/usr/share/openchange/. To reset a user, run the script as root:openchange_user_cleanup username. See the usage output for additional options. -
The "Out of Office Assistant" will not currently work. This feature has not been implemented.
-
Creating folders below INBOX (when not normally permitted by the IMAP server), below the Personal Calendar or Personal Address Book will work in Outlook cached mode but the server-side operation will fail and these folders will never be created. Potentially data loss can occur if the Outlook profile is destroyed. If you wan to create additional top-level mail folders, calendars or address books, open Outlook’s folder list, select the top level node (usually, "email@example.com") and choose "New Folder…" from the contextual menu. Choose the relevant item types.
9.1.2. Mail
-
Sharing mail folders is not supported.
-
To avoid possibly lossy conversion from RTF to HTML, Outlook should be configured to send all mails as HTML (or plaintext) instead of Outlook Rich Text Format.
9.1.3. Calendar
-
Labels will not work.
-
It might be impossible to view event details from a shared calendar. This issue is being worked on.
9.1.4. Tasks
-
Tasks with start/due dates created from Outlook might not appear correctly in SOGo due to a timezone issue.
-
Reminders are not yet supported.
-
Assigning tasks will not work.
9.1.5. Contacts
-
Categories will not work.
-
Distribution lists will not work.
-
Under Microsoft Outlook 2010, the special folder "Suggested Contacts" will not work.
-
The "Offline Address Book" will not work. This feature is not yet supported.
9.1.6. Notes
-
Notes are not synchronized in any ways with SOGo. The current version of SOGo lacks support for notes.
If you notice anything else, please send contact Inverse by sending an email to support@inverse.ca.
10. Additional Information
For more information, please consult the online FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions) :
You can also read the mailing archives or post your questions to it. For details, see :
11. Commercial Support and Contact Information
For any questions or comments, do not hesitate to contact us by writing an email to :
Inverse (http://inverse.ca) offers professional services around SOGo to help organizations deploy the solution and migrate from their legacy systems.